The Ultimate Guide to WordPress User Roles and Permissions
If you have a WordPress site and multiple people manage this site, you need to know about WordPress user roles.
WordPress user roles allow you to define what each user can and can't do on your site. So, knowing how user roles work is crucial for you especially when your site is growing.
Keeping that in mind, today, we are going to discuss everything about WordPress user roles. So, without any further ado, let's get started!
What is WordPress User Role?
A User Role in WordPress is a way to control what different people can do on your website. Each role has a set of permissions that allow users to perform specific tasks.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Access Levels: User roles decide who can access different parts of the WordPress admin area. For example, an administrator can access everything, while a subscriber has limited access.
- Permissions: Each role comes with permissions that let users do certain things, like writing posts, editing content, or installing plugins.
- Hierarchy: User roles are arranged in a hierarchy. Some roles have more permissions than others, helping to organize and secure the site.
- Customization: You can use the default roles or create custom roles to fit the specific needs of your website. This allows you to give users exactly the permissions they need.
WordPress User Roles and Permissions Explained
There are five default user roles available in WordPress by default:
- Administrator
- Editor
- Author
- Contributor
- Subscriber
Now let's get into the details!

1. Administrator
As the name suggests, the Administrator is the most powerful user role and he holds the key to unlocking every door of your website. Users who have this role can do anything they want from the WP dashboard. They can add new pages, posts, plugins, and themes. It also can modify them whenever they want.
They can install, update, and delete plugins. Every single setting is open for the Administrator role. They can manage other users, and change their passwords, information, and also roles. While you are using a site with multiple users, you should carefully assign roles to them.
Administrator Role Explained
- Adding, editing, and deleting users with any user role.
- Managing all content: Adding, editing, publishing, and deleting posts, pages, comments, categories, tags, etc.
- Website settings: Changing themes, installing and activating plugins, modifying website configurations.
- Maintenance tasks: Performing updates, running backups, and managing database operations.
Example: You, the website owner, would be assigned the administrator role to have full control over your website.
2. Editor
Editors can manage the overall content of a WordPress site. If you consider giving this role to a user, he will be able to create pages or posts, edit them, and also trash them. They also have the capability of moderating, editing, and deleting comments.
Basically, editors are responsible for the content, they cannot manage plugins, themes, or settings of your website. However, they can add categories and have access to the media library as well.
Editor Role Explained
- Manage all posts and pages: Create, edit, publish, and delete their own content as well as content created by other users (Contributors and Authors).
- Moderate comments: Approve, edit, or delete comments left by visitors.
- Organize content: Manage categories, tags, and other content taxonomies.
Example: You might assign editor roles to experienced team members who can write, edit, and publish content independently, manage submissions from others, and ensure content quality.
3. Author
Authors can create posts, edit, delete, and publish them. Please note that- they can manage only their own posts. Unlike editors, they don't have the capabilities or permission to manage content created by other users. They cannot create or modify pages.
They can upload files and manage their own uploaded ones. Besides that, they can moderate comments published on their own posts.
Author Role Explained
- Write and edit their own posts: Create drafts, edit them, and publish their own work.
- Upload media: Add images, videos, and other files to their posts.
- View and edit their comments: Manage comments left on their posts.
Example: You might assign author roles to freelance writers or regular content contributors who can focus on creating content without needing access to edit other users' work or manage settings.
4. Contributor
If you want external writers, who will be able to write, edit, and delete drafts, then you should assign them as contributors. These types of users can only write and edit their own posts, but cannot publish them.
An editor or admin must review the posts and publish them if needed. Contributors do not have access to the Media Library and can ask the editor or admin to upload for them.
Contributor Role Explained
- Write and edit their own posts: Create drafts and edit them, but they cannot publish them directly.
- Upload media: Add images and other files to their posts.
Example: You might assign contributor roles to new team members or guest writers who need to submit content for review and approval before publishing.
5. Subscriber
These are general users on your website. They can only read the posts you publish. They get their own profiles and can edit some of their own information. After reading a post, they can also comment.
Subscriber Role Explained
- View published content: Read posts, pages, and comments already published on the website.
- Update their profile information: Change their profile details like email address.
Example: Website visitors who sign up for your newsletter or create an account to access exclusive content would typically be assigned the subscriber role.
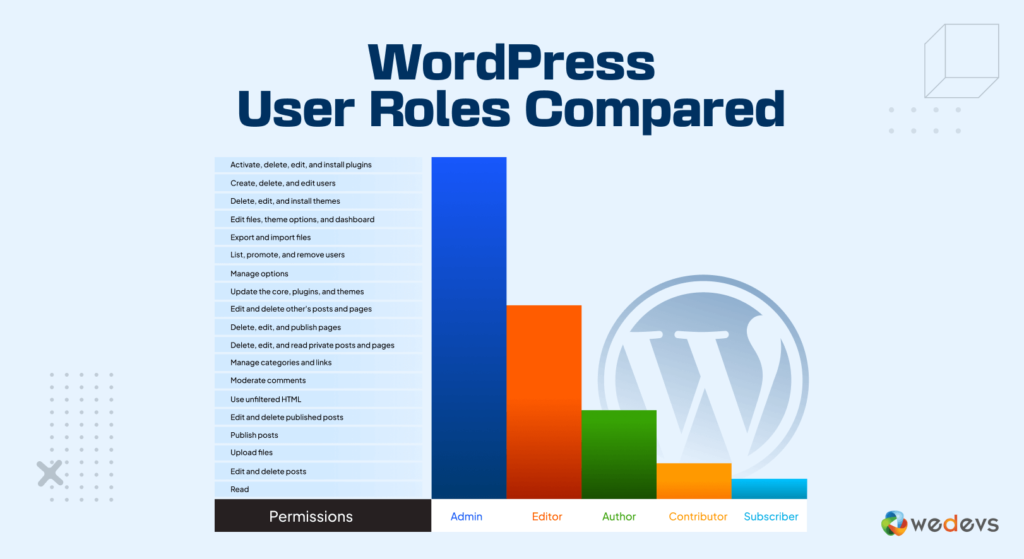
WordPress User Roles and Permissions Explained
Now check this image to understand the capabilities and permissions of each user role in a WordPress site:
How to Manage WordPress User Roles and Permissions
In this segment, we will show you how to add, remove, or update an existing user role. Let's discuss that!
I) How to Add Someone to a User Role
Suppose, you want to add someone to a specific user role, e.g., Editor. Let's check how you can do that.
First, log in to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Users -> All Users. Now click on the Add New User option.
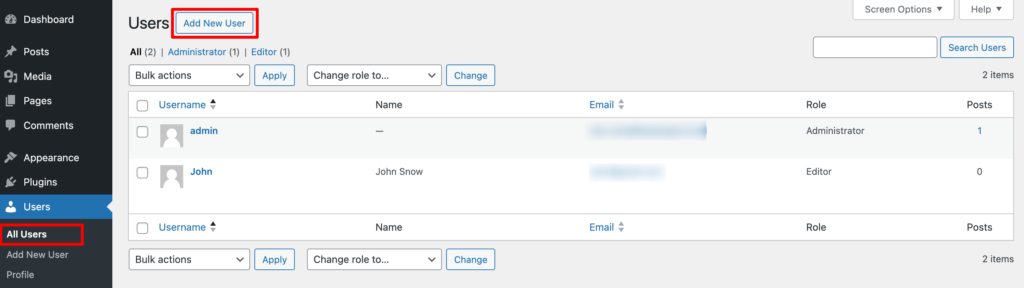
There you will find the options to add the user's information. Finally, choose the role from the Role option and click on the “Add New User” button to save this user.
That's how you can add someone to a specific role.
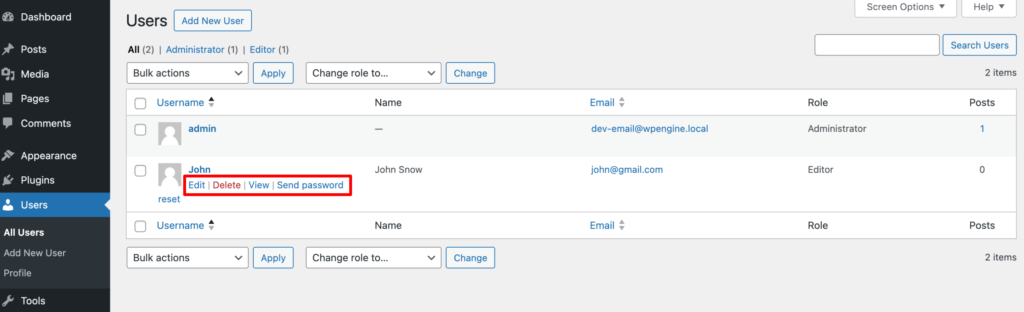
II) Remove Someone from an Assigned Role
Go to Users -> All Users and find which user you want to remove. Just click on the Delete button to remove that user.
III) How to Update a User Role
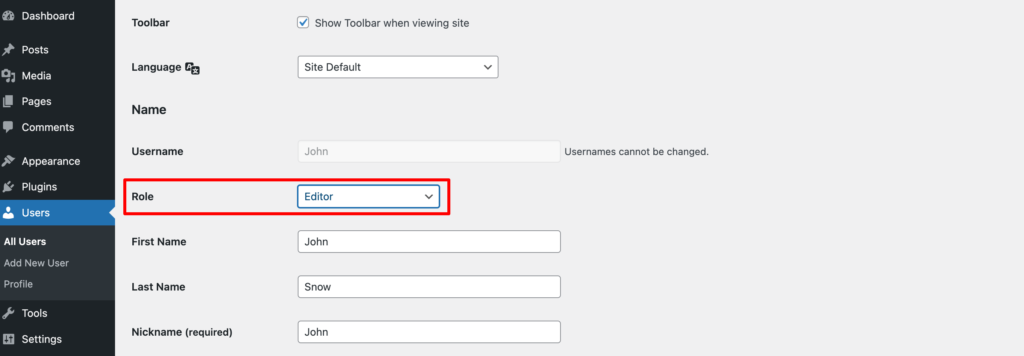
Let's imagine, you assigned someone as Editor, now you want to set his role as Contributor.
Go to Users -> All Users and find which person's user role you want to update. Click on the Edit button and set his role as Contributor from the Role option. Finally, click on the “Update User” to save the changes.
Are you looking for something else?
If you are looking for how to add custom roles in WordPress, we have got you covered. We have a step-by-step tutorial on that, check it out here.
How to Add Custom User Roles on Your WordPress Site (Plugin+Code)
Wrapping up the WordPress User Roles and Permissions
Understanding WordPress user roles and permissions is essential for effectively managing your website. By assigning the appropriate roles, you can ensure that users have the right level of access to perform their tasks without compromising the security or functionality of your site.
Here’s a quick recap:
- Administrators have full control over the site.
- Editors manage and publish content, including posts by other users.
- Authors can write and publish their own posts.
- Contributors can write and edit their own posts but need approval to publish.
- Subscribers can manage their profiles and view content.
With a clear understanding of user roles, you can empower your team and keep your WordPress website running smoothly.
Now if you have any confusion, feel free to share that with us using the comment box below. We are all ears. Take care!